Introduction
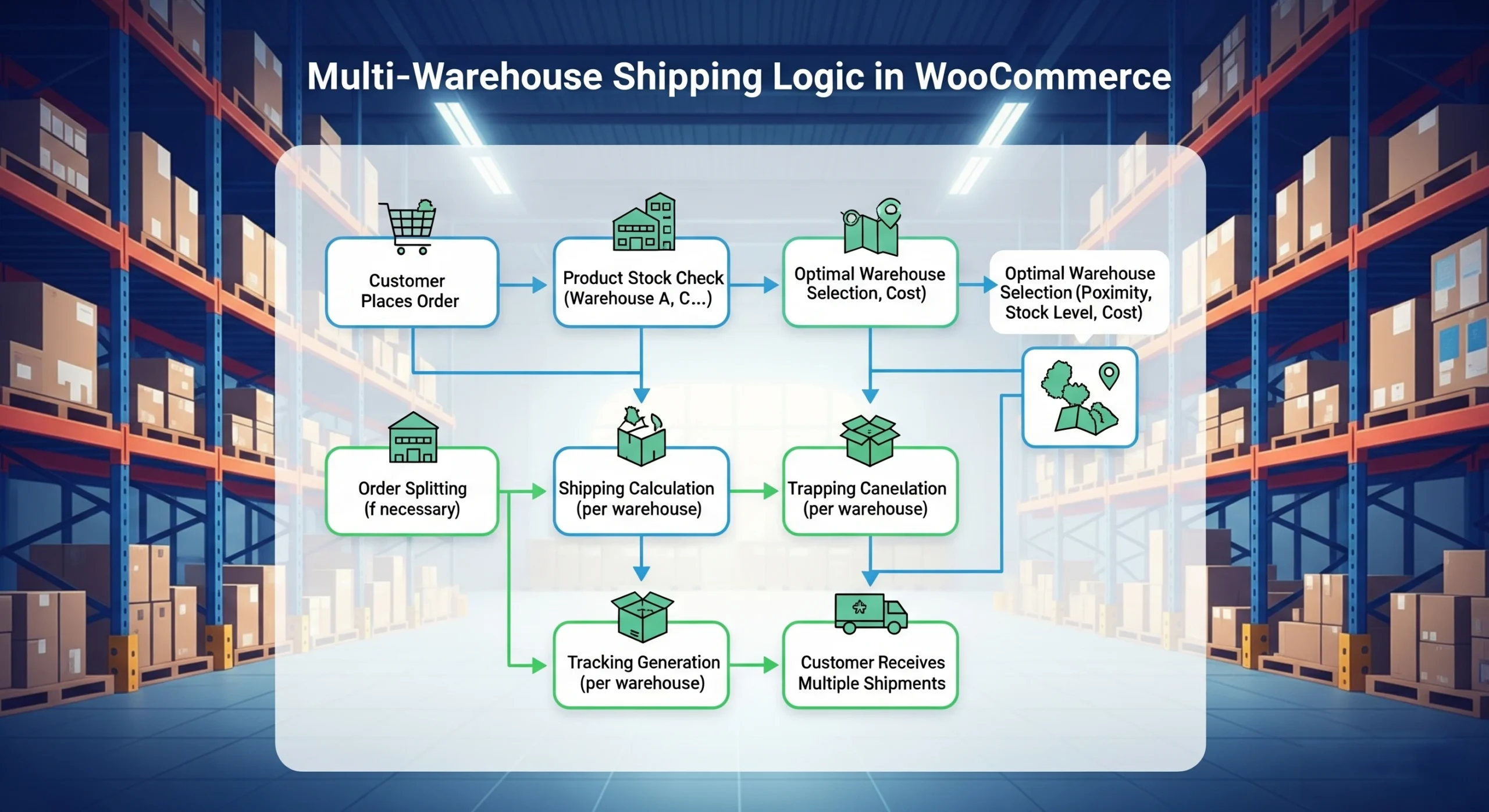
As your WooCommerce store scales, you may need to manage multiple warehouses or fulfillment centers. By default, WooCommerce uses a single inventory location, which isn’t practical for:
- Multi-warehouse setups
- Dropshipping vendors
- Regional shipping rules
In this guide, you’ll learn how to build multi-warehouse shipping logic for WooCommerce, including inventory allocation, cost calculation, and custom shipping rules.
Why Multi-Warehouse Shipping?
- Faster delivery by fulfilling from the nearest warehouse
- Reduced shipping costs
- Better inventory management
- Support for vendor-based fulfillment (multi-seller marketplaces)
Tools & Requirements
- WooCommerce (latest version)
- Knowledge of WordPress hooks and filters
- Optional:
- WooCommerce Multi-Location Inventory Plugins
- Action Scheduler for background stock updates
- Custom shipping methods
Step 1: Storing Warehouse Locations
You can use custom post types or options to define warehouses:
register_post_type('warehouse', [
'label' => 'Warehouses',
'public' => false,
'show_ui' => true,
'supports' => ['title', 'custom-fields'],
]);
Each warehouse can have:
- Name
- Address
- Stock levels (linked to products)
- Shipping zones
Step 2: Assigning Stock Per Warehouse
Add stock meta for each warehouse:
update_post_meta($product_id, 'warehouse_stock_ny', 50);
update_post_meta($product_id, 'warehouse_stock_la', 30);
You can also use a custom table for performance if you manage thousands of products.
Step 3: Determining Nearest Warehouse
Hook into WooCommerce checkout to select the warehouse based on customer location:
function bookwp_get_nearest_warehouse($customer_state) {
$warehouses = [
'NY' => 'New York Warehouse',
'CA' => 'Los Angeles Warehouse',
];
return $warehouses[$customer_state] ?? 'Default Warehouse';
}
Step 4: Custom Shipping Calculation
Override shipping costs dynamically:
phpCopyEditadd_filter('woocommerce_package_rates', 'bookwp_dynamic_shipping_rates', 10, 2);
function bookwp_dynamic_shipping_rates($rates, $package) {
$customer_state = WC()->customer->get_shipping_state();
$warehouse = bookwp_get_nearest_warehouse($customer_state);
foreach ($rates as $rate_key => $rate) {
if ($warehouse === 'Los Angeles Warehouse') {
$rates[$rate_key]->cost += 5; // extra west-coast handling fee
}
}
return $rates;
}
Step 5: Splitting Orders Across Warehouses
If a single order needs multiple warehouses:
- Split the cart into multiple shipments
- Create sub-orders for each warehouse using
wc_create_order() - Reduce stock per warehouse
add_action('woocommerce_checkout_create_order', function($order) {
// Logic to split order by warehouse
});
Bonus: ERP / API Integration
For large operations:
- Sync inventory from ERP (Odoo, NetSuite, SAP)
- Use webhooks or REST API to update stock levels automatically
- Trigger fulfillment requests per warehouse
Advanced Enhancements
- Action Scheduler: Schedule stock sync jobs
- Distance Calculation: Use Google Maps API for warehouse proximity
- Dropshipping Support: Send vendor-specific email notifications
- Performance: Use custom DB tables instead of post meta for speed